Pneumonia is a common but potentially serious infection that affects the lungs. Despite advances in medicine, it continues to impact millions of people worldwide each year. Understanding what pneumonia is, how it develops, and the available treatment options is crucial for protecting your health and recognizing symptoms early. This article provides a comprehensive overview of pneumonia, from its causes and risk factors to prevention strategies and treatment approaches.
What Is Pneumonia?
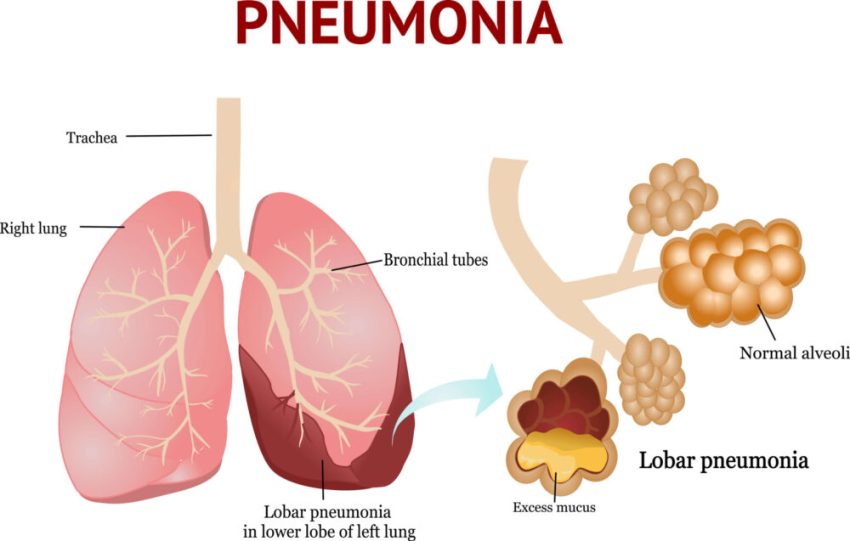
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs (alveoli) in one or both lungs. These tiny sacs normally fill with air when you breathe, allowing oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. When pneumonia occurs, the alveoli fill with pus, fluid, or debris, making breathing difficult and reducing oxygen intake. Depending on the severity, pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening.
Causes of Pneumonia
Several different microorganisms can cause pneumonia, each leading to slightly different forms of the illness.
Bacterial Pneumonia
The most common cause is bacteria, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae. This type often follows colds or the flu when the immune system is weakened. Bacterial pneumonia can develop suddenly, with high fever, chills, and chest pain.
Viral Pneumonia
Viruses such as influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and even coronaviruses can cause pneumonia. Viral pneumonia is usually milder than bacterial pneumonia but may become severe in vulnerable groups.
Fungal Pneumonia
Less common but still serious, fungal pneumonia occurs when fungi from soil or bird droppings are inhaled. People with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk.
Aspiration Pneumonia
This type develops when food, liquids, or vomit accidentally enter the lungs. Aspiration pneumonia is more likely in individuals who have swallowing difficulties or neurological disorders.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Recognizing symptoms early can help prevent complications. Symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity but often include:
- Persistent cough (sometimes producing green, yellow, or bloody mucus)
- Fever and chills
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Confusion (especially in older adults)
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea in some cases
It is important to note that mild pneumonia symptoms can resemble those of the flu or a bad cold, which sometimes delays proper diagnosis.
Who Is at Risk?
While anyone can develop pneumonia, certain groups are more vulnerable:
- Infants and young children with developing immune systems
- Adults over the age of 65
- People with chronic illnesses such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease
- Smokers and individuals exposed to secondhand smoke
- Patients with weakened immunity due to HIV, cancer treatment, or organ transplants
How Pneumonia Is Diagnosed
Doctors typically diagnose pneumonia through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and tests. A stethoscope can reveal abnormal crackling or bubbling sounds in the lungs. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and sputum cultures confirm the type of pneumonia and help guide treatment.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
Treatment depends on the cause, severity, and the patient’s overall health.
Antibiotics
For bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are the primary treatment. It’s crucial to complete the entire prescribed course even if symptoms improve early to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Antiviral Medications
When pneumonia is caused by viruses like influenza, antiviral drugs may be prescribed. However, most viral pneumonia cases resolve with rest, fluids, and supportive care.
Antifungal Drugs
Fungal pneumonia requires antifungal medication, often for an extended period.
Supportive Care
For mild cases, rest, fluids, fever reducers, and over-the-counter pain medication can be enough. Severe cases may require hospitalization, oxygen therapy, or intravenous antibiotics.
Possible Complications
If left untreated or if the infection is severe, pneumonia can lead to complications such as:
- Bacteremia: When bacteria spread from the lungs into the bloodstream, potentially leading to septic shock.
- Lung Abscesses: Pockets of pus that form in the lungs.
- Pleural Effusion: Fluid buildup around the lungs.
- Respiratory Failure: Severe cases may require mechanical ventilation.
These complications highlight the importance of seeking medical attention promptly if pneumonia is suspected.
Preventing Pneumonia
Prevention plays a vital role in reducing pneumonia cases worldwide.
Vaccination
The pneumococcal vaccine helps protect against the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia. Influenza vaccines also reduce the risk of viral pneumonia triggered by the flu. Vaccines are especially important for older adults, children, and people with chronic illnesses.
Good Hygiene
Washing hands regularly, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals help limit the spread of germs.
Healthy Lifestyle
A strong immune system can better fight infections. Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and avoiding smoking can all reduce pneumonia risk.
Medical Management
For people with chronic conditions, properly managing illnesses such as diabetes or asthma can lower susceptibility.
Living with and Recovering from Pneumonia
Recovery from pneumonia varies depending on age, health, and the type of infection. Some people may feel better within a week, while others may experience fatigue and cough for several weeks. During recovery, it is important to:
- Get plenty of rest and avoid overexertion
- Drink enough fluids to loosen mucus
- Follow the prescribed treatment plan carefully
- Attend follow-up medical appointments to ensure full recovery
A Closer Look at Pneumonia’s Global Impact
Pneumonia remains one of the leading causes of hospitalization worldwide, particularly among children under five and adults over sixty-five. The World Health Organization reports that pneumonia is responsible for millions of deaths every year, many of which are preventable with vaccines, better healthcare access, and awareness campaigns.
Breathing Easier: The Key to Protecting Your Lungs
Pneumonia may sound intimidating, but knowledge is one of the best defenses. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, taking preventive measures, and following medical advice, individuals can significantly reduce their risk. Stronger lungs and better immunity come not only from medicine but also from healthy daily choices. Protecting your respiratory health today means breathing easier tomorrow.